Table of Contents
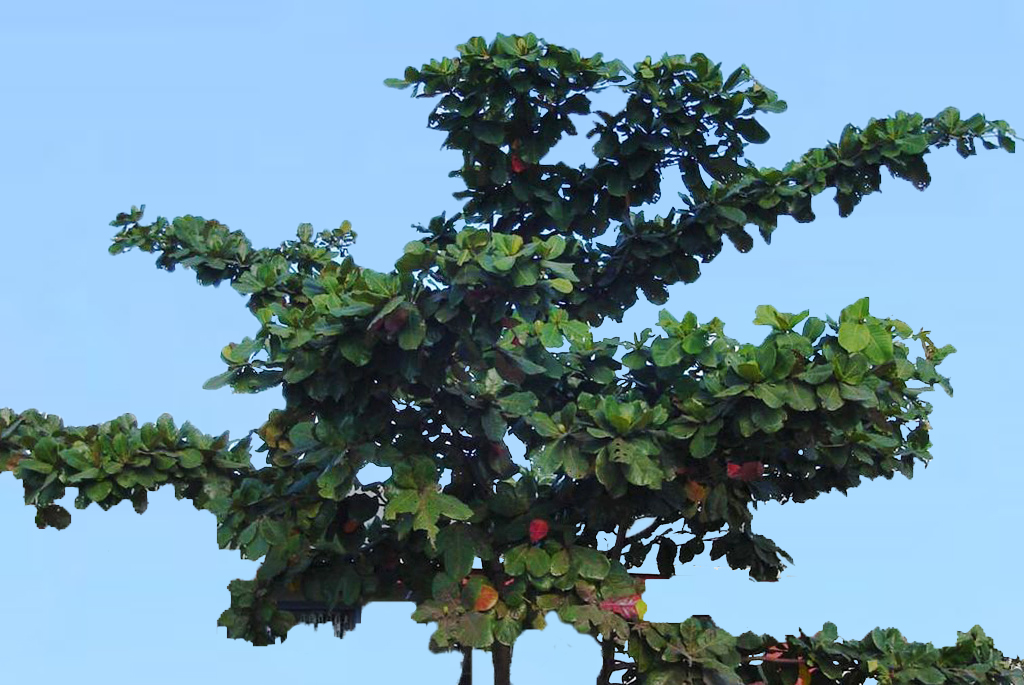

1. What is it?
Terminalia catappa, known as the Sea Almond tree, is a common coastal tree species in the family Combretaceae. It is widely distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world, and can be recognized by its distinct tiered branching. The trees are highly useful as they provide important economical, medical and environmental benefits to the local communities which they are found in.
Scientific name – Terminalia catappa L.
Common names – Sea Almond, Indian Almond, Tropical Almond, Ketapang, 榄仁树
2. What's in a name?
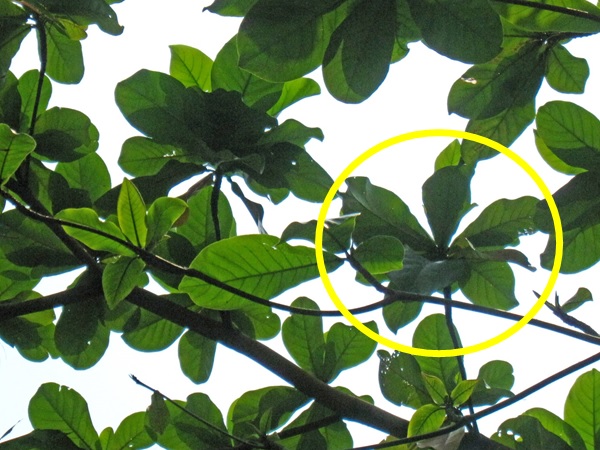
This genus of trees derives its Latin name, Terminalia, from the position of its leaves, which are spirally clustered at the end of its branches.

3. Ecology & Biology
3.1 Growth conditions
It is commonly found along the coastal and wetland areas. Thus, it has a high tolerance to salinity, high light intensity/drought and windy conditions. It is also able to grow in sandy or loamy soils, in media that are either acidic or alkaline. Its seeds are adapted to water dispersal by oceanic currents as they are very light and buoyant [1].3.2 Pollination
Flowers of this tree produce traces of nectar and large amounts of pollen, thus they are pollinated by insects such as stingless bees (Trigona sp.) and honey bees (Apis sp.) [2].3.3 Dispersal
The fruits of the Sea Almond are dispersed by water. They are very lightweight and have a fibrous husk which allows them to float on water once they fall into the sea. They are able to survive floating on water for a few months, carried by the ocean currents to another suitable shore before it germinates [1].Besides this abiotic dispersal method, the fruits of the Sea Almond tree may also be eaten and dispersed by bats.
4. Where can the trees be found?
4.1 Native range
The Sea Almond tree is a perennial tree species which is widely distributed throughout tropical Asia (Southeast Asia, India) to North Australia and Polynesia (South Pacific region). It is usually associated with tropical coastal habitats such as tropical beach forests, rocky and sandy beaches and even at the edges of mangrove swamps.Native to East Indies and Oceania and now found throughout the Tropics including Myanmar, Cambodia and Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia and the Philippines [3].
4.2 In Singapore
The Sea Almond tree is common along coastal areas such as Changi Beach, East Coast Park and Labrador Park. However, they may also be cultivated along roadsides and in parks in urban environments for ornamental purposes and to provide shade with their distinct pagoda-like shape and moderately large leaves.Local conservation status: Common / Native of Singapore [4].
4.3 Global distribution
Being adapted to growing in a wide range of substrates and in the presence of harsh abiotic conditions, the Sea Almond tree readily naturalizes in suitable tropical littoral habitats. This makes them a potential weed threat to native plant communities since they may out-compete other slow-growing endemic species [5].Map showing global distribution of the Sea Almond tree: native range (red pins), distribution in Singapore (yellow pins) and naturalized ranges (green pins).
5. How do I identify a Sea Almond tree?
5.1 Size
Maximum height: 15 - 30 m
Diameter at breast height (d. b. h.): About 1.5 m
5.2 Leaves
Fun fact! The Sea Almond tree is deciduous and it sheds its leaves twice a year [4]. Their leaves turn red/yellow in colour as the plant draws nutrients back from its leaves for recycling before they are shed.

| Type |
|
| Shape |
|
| Size |
|
| Arrangement |
|
| Texture |
|
5.3 Flowers
Fun fact!
The flowers of the Sea Almond tree are bisexual, meaning that there are both male and female flowers on the same plant!Such plants usually have biological mechanisms that prevent self-fertilization from occurring.
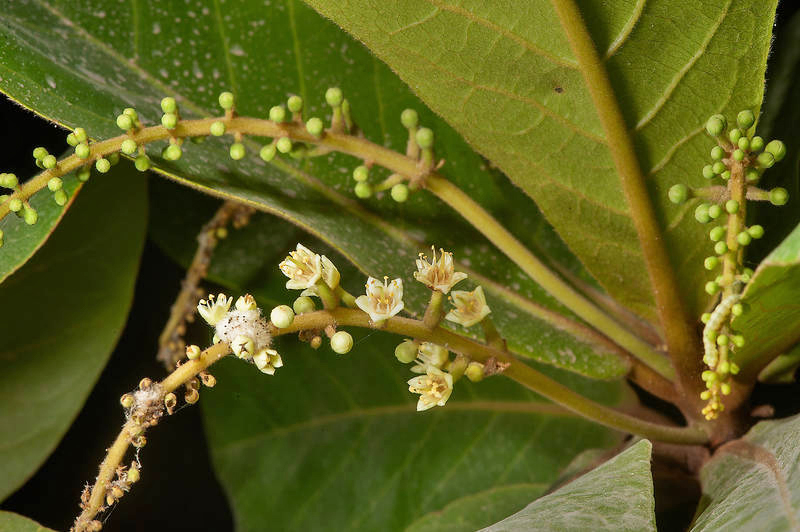
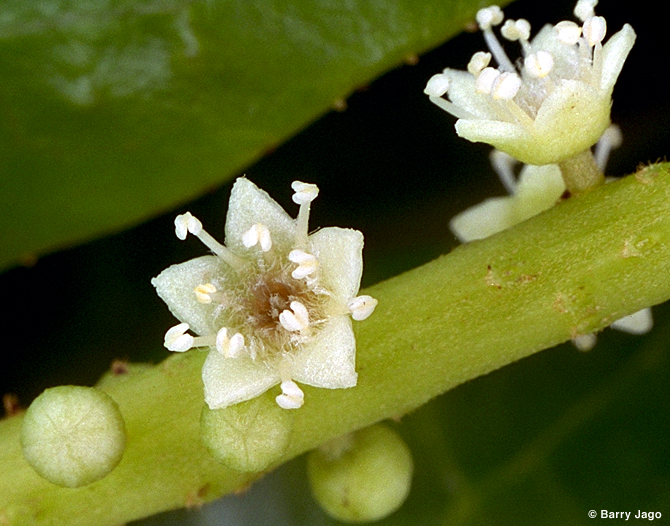


Figure 4. (Left) An inflorescence of Sea Almond flowers. Used with permission. © Alexey Sergeev
(Right) Close-up of a single Sea Almond flower. Used with permission. © Barry Jago
| Location |
|
| Arrangement |
|
| Size |
|
| Colour |
|
| Stamen |
|
| Petals |
|
| Position of ovary |
|
| Position of male and female flowers |
|
5.4 Fruits
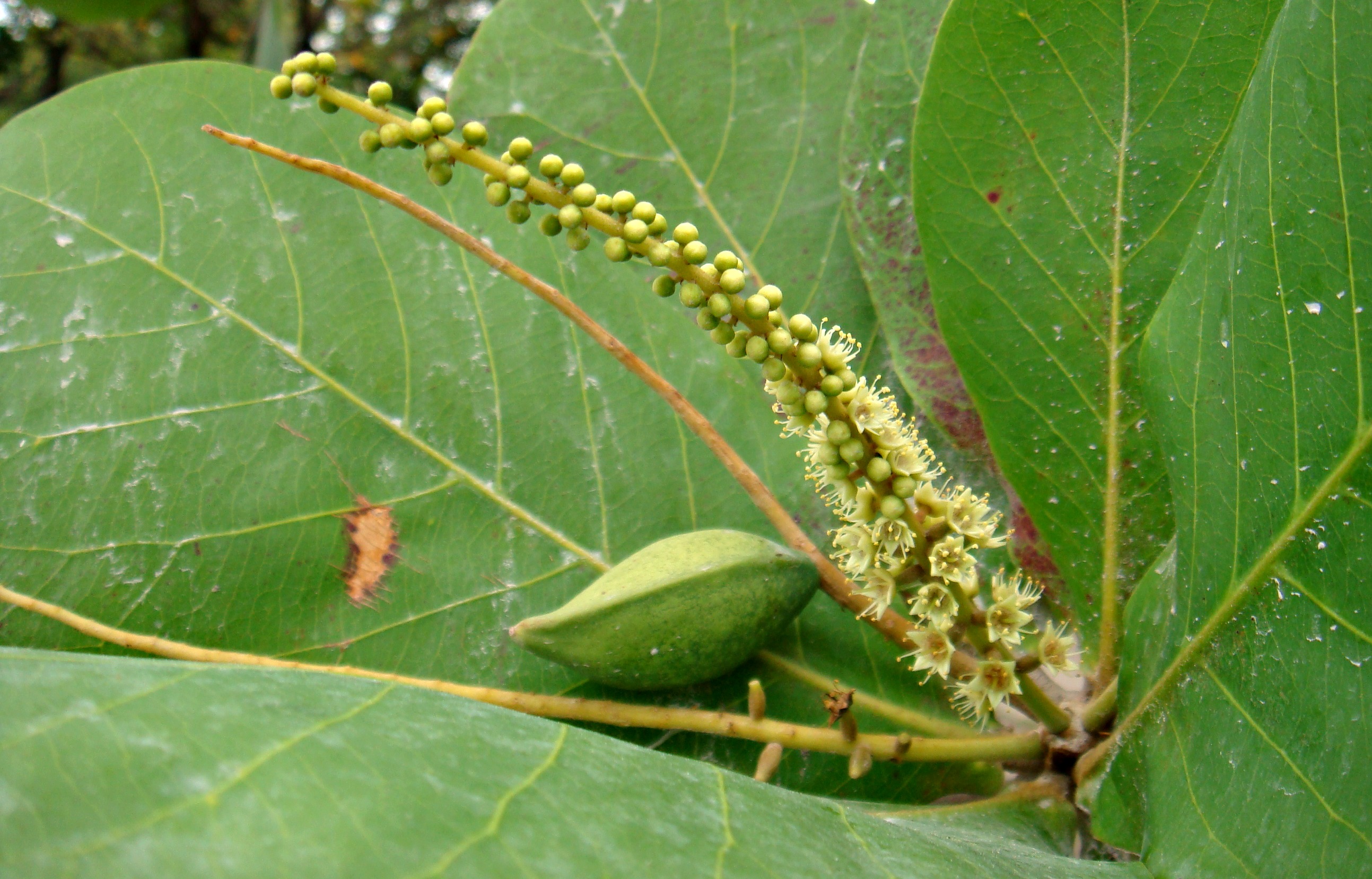
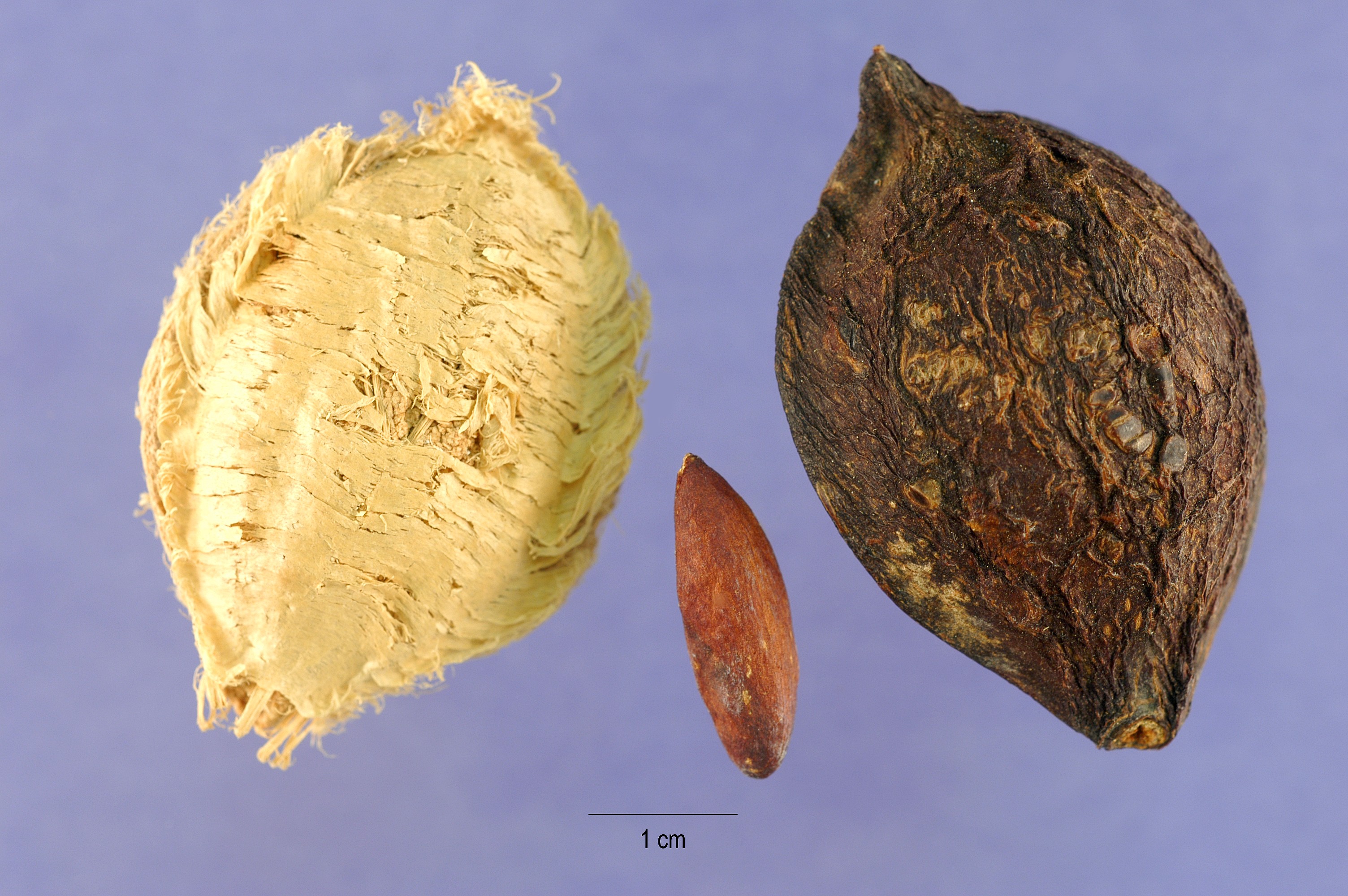


Figure 5. (Left) A single Sea Almond fruit. Used with permission. © CameliaTWU
(Center) Dried Sea Almond fruit and a single kernel. Used with permission. © Steve Hurst
(Right) Fresh fruit of the Sea Almond tree with partial exocarp. © Emily Chua
| Description |
|
| Shape |
|
| Size |
|
| Stalk |
|
| Colour |
|
6. One tree, many uses
Fun fact!
The dried leaves of the Sea Almond tree, also known as Ketapang leaves, are very popular as a natural medicine and water conditioner for aquarium use because of their anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties.
Food |
The kernel within the Sea Almond fruit is edible and tastes like almond nuts, where the plant derives its common name. Similarly, the oil extracted from the kernel is similar to almond oil. The kernel has a relatively high protein content and is used as a substitute for oils such as groundnut and cottonseed oil [8]. Figure 6. Photo of the Sea Almond fruit at various stages of ripeness. Fruit in the middle has been sawn into half to reveal the kernel within. Photo licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 3.0 Unported License. |
Medicinal / Pharmaceutical |
Extracts of the flowers, fruits, bark, leaves and stem of the Sea Almond tree have long been used in traditional folk medicine to treat common diseases and ailments such as malaria and diabetes. For example, the oil extracted from the seeds of the Sea Almond tree can be used to relieve abdominal inflammations. In Africa, the leaves of the Sea Almond tree are known to have anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory properties. Current studies have been done to further confirm the medicinal properties and active compounds in the plant. Extracts of Sea Almond fruits produced significant anti-diabetic activity in diabetic rat models [9]. In addition, the extracts of the leaves of the Sea Almond tree have been demonstrated to have hepato-protective and anti-oxidant functions and contain compounds such as hydrolysable tannins and triterpenoids [10]. Soaking dried leaves in water of the Sea Almond tree lowers the pH of the aquarium tank water and releases anti-bacterial and anti-fungal compounds.These compounds also promote spawning in fish species and the healing of fungal fin rots in fish. This has potential applications in the area of aquaculture since studies has shown that adding leaf extracts of T. catappa can reduce fungal infections in the eggs of the economically important food fish, tilapia [11].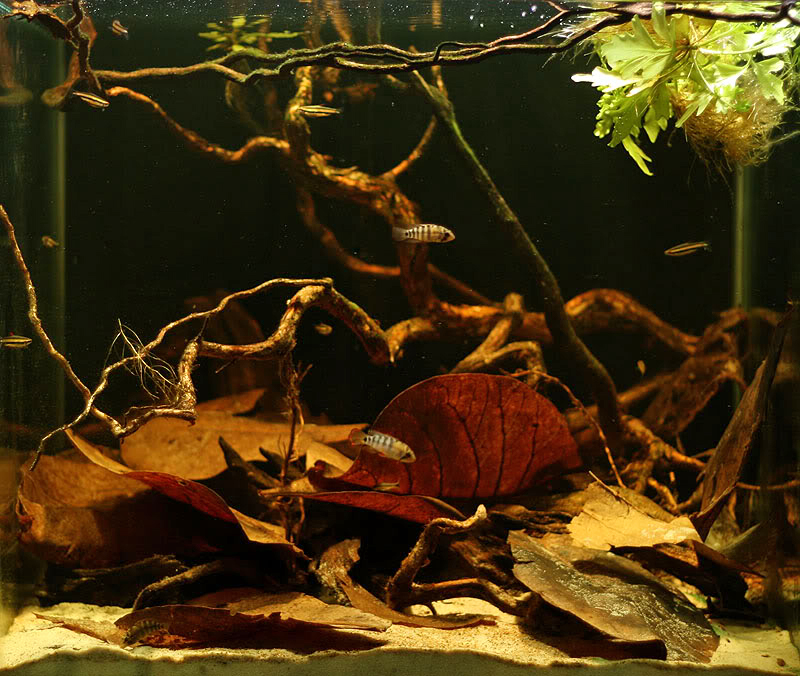  Figure 7. Dried Sea Almond leaves used in aquariums to lower the pH of the water and provide anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties. Photo credit: © AquaBid.com |
Functional |
The trees are planted in countries and utilized by the local community for a variety of household uses, such as firewood and timber as raw materials for making furniture, wooden flooring and even boats in some developing countries. The bark, fruits and sometimes leaves of the tree are used as a source of tannins. Tannins are chemical compounds which can be used to dye materials such as cotton and rattan to brown, orange or red colour [6]. In addition, the bark of the Sea Almond tree is also a source of resin for making varnishes and adhesives. |
Environmental benefits |
Terminalia is related to other mangrove taxa in the same family such as Lumnitzera and Languncularia. As such, they also provide the same ecosystem service of coastal stabilization since they usually grow by the coastal areas and thus help to protect the coastline from erosion by constant wave action [1].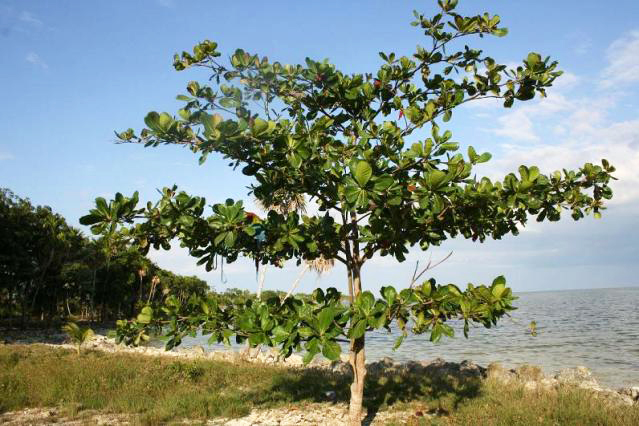 Figure 8. Photo of the Sea Almond tree along the coast. Photo licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 3.0 Unported License. |
7. A lookalike tree?
The Sea Almond tree may be confused with another similar-looking tree, known as the Cabbage Tree in Singapore (Fagraea crenulata Maingay ex C.B. Clarke, Gentianaceae).




Figure 9. (Top center) Full height of the Fagraea crenulata tree. (Bottom left) Small thorns on the surface of the trunk of the tree.
(Bottom center) Inflorescence of the tree. (Bottom right) Cluster of fruits of the tree. Photos used with permission.
© uforest.org
| Height of tree |
|
| Habit |
|
| Leaves |
|
| Trunk |
|
| Flowers |
|
| Fruits |
|
| Distribution |
|
8. Taxonomy & Systematics
8.1 Classification
Kingdom – Plantae
Division – Trachaeophyta
Class – Magnoliopsida
Order – Myrtales
Family – Combretaceae
Genus – Terminalia
Species – Terminalia catappa L.
A more detailed version of the taxonomic classification of T. catappa can be found on the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS).
Did you know?A single organism may be described more than once by different people! In such cases, the first description of the species would be retained as the formal name and the subsequent descriptions would be referred to as synonyms.
8.2 Synonyms
Badamia commersonii Gaertn. (1790)
Buceras catappa Hitchc. (1893)
Juglans catappa Lour. (1790)
Myrobalanus catappa Kuntze (1891)
Terminalia procera Roxb. (1811)
More information on the synonyms of T. catappa here.
8.3 DNA barcodes
Two choloroplast genes, matK and rbcL have been sequenced for T. catappa and are available for download from GenBank via the links.
8.4 Phylogeny
Few studies have been done to resolve the complex phylogenetic relationships within the family Combretaceae. Plastid and nuclear sequences have been used to reconstruct the phylogeny within the family Combretaceae. According to one such study done by Maurin et. al (2010), it is suggested that the genus Terminalia forms a paraphyletic group. The bootstrap values of T. catappa are low, thus its clade is not present in the strict consensus tree [14].
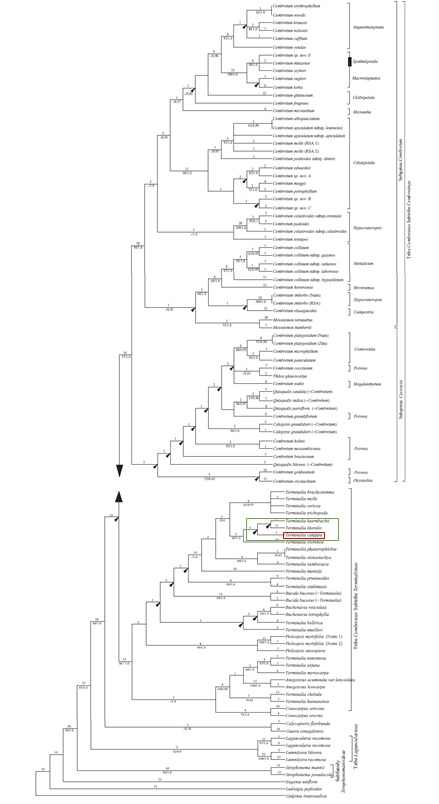
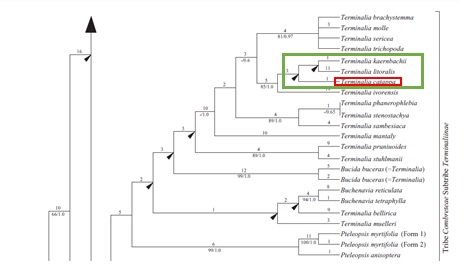
Figure 10. (Top) One of the equally parsimonious trees based on the combined plastid data. T. catappa is boxed up in red box. Arrows indicate clades that are not present in the strict consensus tree (in green box). (Bottom) Zoomed in phylogenetic tree. Photo credit: Olivier Maurin (Permission pending).
8.5 Type information
Terminalia catappa was first described by Linnaeus in Systema Naturae, ed. 12, 2: 674, in 1767. Subsequently, a lectotype (LINN-1221.1) for T. catappa was designated and deposited in the Natural History Museum, London.
9. Glossary
10. Useful links
- USDA Plant Database
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Electronic Plant Information Centre of Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
- NParks Flora Fauna Web
11. Literature and References
[1] Encyclopaedia of Life, 2012. Terminalia catappa: Indian Almond. http://eol.org/pages/582724/overview (Accessed 7 Nov.2014)
[2] Atluri, J. B., C. Subba & S. P. Venkata, 2003. Breeding and pollination systems in the Indian Almond tree Terminalia catappa. Ecology, Environment and Conservation. 9(3): 331-335.
[3] Jensen, M., 2001. Trees and fruits of Southeast Asia: An illustrated field guide. Orchid Press, Bangkok.
[4] National Parks Board, Singapore, 2013. Terminalia catappa L. https://florafaunaweb.nparks.gov.sg/Special-Pages/plant-detail.aspx?id=2894 (Accessed 23 Oct.2014).
[5] Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council, 2009. Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council Invasive Plant Lists. http://www.fleppc.org/list/list.htm (Accessed 25 Oct.2014)
[6] Rao, A., & Y. C, Wee, 1989. Singapore trees. Singapore Institute of Biology, Singapore. 311 pp.
[7] Wee, Y. C., 1989. A guide to the Wayside trees of Singapore. Singapore Science Centre, Singapore. 86 pp.
[8] Selvam, V., 2007. Trees and shrubs of the Maldives. Ministry of Fisheries, Agriculture, and Marine Resources, Maldives. pp. 165-166
[9] Nagappa A.N., P.A. Thakurdesai, N. Venkat Raob & J. Singh, 2003. Antidiabetic activity of Terminalia catappa Linn fruits. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 88: 45-50.
[10] Kinoshitaa, S., Y. Inouea, S. Nakamaa, T. Ichibab, & Y. Aniyaa, 2007. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective actions of medicinal herb, Terminalia catappa L. from Okinawa Island and its tannin corilagin. Phytomedicine, 14: 755–762
[11] Reverter, M., N. Bontemps, D. Lecchini, B. Banaigs & P. Sasal, 2014. Use of plant extracts in fish aquaculture as an alternative to chemotherapy: Current status and future perspectives. Aquaculture, 433: 50-61.
[12] Keng, H., & R. Keng, 1990. The concise flora of Singapore: Gymnosperms and dicotyledons. Singapore University Press, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
[13] Corner, E. J. H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya (4th ed.). Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur. 217 pp.
[14] Maurin, O., M. W. Chase, M. Jordaan & M. Van der Bank, 2010. Phylogenetic relationships of Combretaceae inferred from nuclear and plastid DNA sequence data: implications for generic classification. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 162: 453–476